Category: Technologies
Posted by: bagheljas
RedHat OpenShift availability on IBM Z opens up the Economical door for the Enterprise Applications Modernization with IBM Z. RedHat OpenShift capability of deploy once and run anywhere provides the opportunity to the CIOs to deliver the flexibility to Switch Economically either Server Platform or Cloud providers as industry evolve. In next 10 years, we will experience and benefit from the brand new usage of the IBM Z Server platform.
First, deploy distributed workloads on IBM Z that needs unmatched uptime and performance that is not economical on x86 server platform. Second, let the IBM Z provides the side by side deployment capability to deploy Windows and Linux Virtual Machines and Containers workloads using RedHat OpenShift on IBM Z for the economical iterative application modernization.
The core feature "Deploy Once and Run Anywhere" of the RedHat OpenShift enables users to switch to the industry leading platform providers anytime and anywhere.
First, deploy distributed workloads on IBM Z that needs unmatched uptime and performance that is not economical on x86 server platform. Second, let the IBM Z provides the side by side deployment capability to deploy Windows and Linux Virtual Machines and Containers workloads using RedHat OpenShift on IBM Z for the economical iterative application modernization.
The core feature "Deploy Once and Run Anywhere" of the RedHat OpenShift enables users to switch to the industry leading platform providers anytime and anywhere.
Category: Technologies
Posted by: bagheljas
Category: Technologies
Posted by: bagheljas
For implementing business process agility using Oracle SOA BPEL Process Manager, most books cover few of the following domains:
In this book, we have combined these domains to deliver the complete handbook. It provides our readers an understanding of what goes outside of their direct responsibilities. This horizontal understanding improves the collaboration among the cross functional groups that would result in increased team productivity. You can preview and buy the book at
- Designing and architecting SOA composite applications
- Developing SOA composite applications using BPEL
- Testing and debugging SOA composite applications
- Installing, configuring, deploying, securing, and administering SOA composite applications
In this book, we have combined these domains to deliver the complete handbook. It provides our readers an understanding of what goes outside of their direct responsibilities. This horizontal understanding improves the collaboration among the cross functional groups that would result in increased team productivity. You can preview and buy the book at
 | It is also available at LYBRARY, Computer Manuals, and most internet book retailers. You will find an overview of technical fundamentals, step-by-step tutorials, and industry leading practices implementing SOA composite applications. |
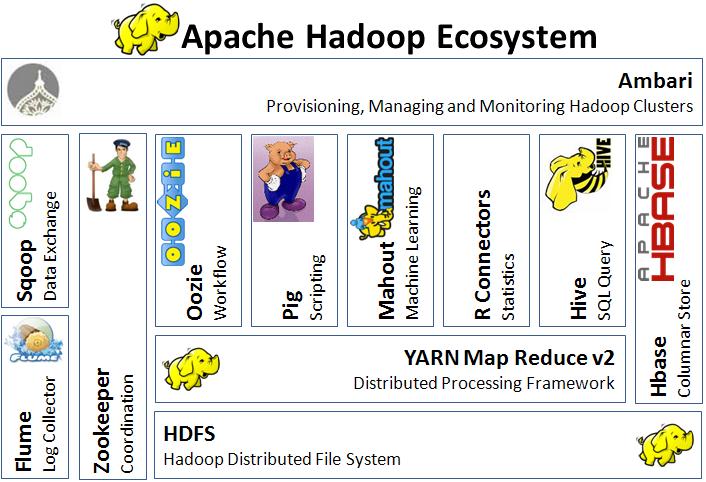
06/15: Apache Hadoop Ecosystem
Category: Technologies
Posted by: bagheljas
02/07: Mass Data Storage System
Category: Technologies
Posted by: bagheljas
Mass Data Storage System is mission critical component for modern day’s deployment of Server Technology Platform in traditional, virtualization and cloud deployment models. Mass Data Storage System is also known as secondary and/or tertiary storage may connect to server technology platform using computer networks. The characteristics of these networks categorize the Mass Data Storage System as Direct Attached Storage (DAS), Network Attached Storage (NAS) and Storage Area Network (SAN).
The DAS is connected to server hardware via internal network / bus of the server hardware platform also known as traditional mass storage; that provides the best possible performance but lowest in flexibility for sharing and growth. DAS is still the most popular approach of implementing Mass Data Storage System for users that has well defined fixed requirements, tight budgets with high performance needs.
The NAS is attached to a computer which another computer can access at file level over a Local Area Network (LAN), a private Wide Area Network (WAN), or over the Internet. NAS is commonly associated with the NFS and CIFS/SMB protocols. The performance on NAS is dependent on the LAN, WAN or Internet but provides the flexibility to access from anywhere economically. The best use case for NAS is providing mass storage over WAN, Internet and Cloud Offering.
The SAN is a specialized network that is commonly associated with Fiber Channel Networks that provides other computers the mass storage capacity that is capable of matching the performance of DAS. The SAN provides the storage access at the block-addressing (raw) level, leaving it to attaching systems to manage data and file systems within the provided capacity. SAN is the modern day technology to provide flexible on-demand disk space for a server deployed in traditional, virtualization and cloud deployment models. The cost of implementing SAN is offset by the flexibility and performance it provides to an organization to meet the unknown demands and re-usability at the ease.
The DAS is connected to server hardware via internal network / bus of the server hardware platform also known as traditional mass storage; that provides the best possible performance but lowest in flexibility for sharing and growth. DAS is still the most popular approach of implementing Mass Data Storage System for users that has well defined fixed requirements, tight budgets with high performance needs.
The NAS is attached to a computer which another computer can access at file level over a Local Area Network (LAN), a private Wide Area Network (WAN), or over the Internet. NAS is commonly associated with the NFS and CIFS/SMB protocols. The performance on NAS is dependent on the LAN, WAN or Internet but provides the flexibility to access from anywhere economically. The best use case for NAS is providing mass storage over WAN, Internet and Cloud Offering.
The SAN is a specialized network that is commonly associated with Fiber Channel Networks that provides other computers the mass storage capacity that is capable of matching the performance of DAS. The SAN provides the storage access at the block-addressing (raw) level, leaving it to attaching systems to manage data and file systems within the provided capacity. SAN is the modern day technology to provide flexible on-demand disk space for a server deployed in traditional, virtualization and cloud deployment models. The cost of implementing SAN is offset by the flexibility and performance it provides to an organization to meet the unknown demands and re-usability at the ease.
09/09: DNS Cache
Category: Technologies
Posted by: bagheljas
DNS Cache is critical part of the whole process of mapping a site domain and/or internet service address to IP address. It is created to improve performance and reduce the DNS queries served by the ROOT Name Servers, Top Level Registrars and DNS Authoritative servers and DNS caching supported the design and it is cached at every hop involves in the process.
The minimum hops for resolving a site domain suchna.com are ROOT Name Servers, Top Level Registrars, DNS Authoritative Servers, DNS Name Resolvers and Client Machines.
The Time To Live(TTLs) settings at the DNS Authoritative Server or also referred as Master DNS Server / SOA owner for a site domain and/or internet service address recommends the client machines and DNS name resolvers for refreshing intervals for a name to IP address mapping.
The settings at the client machines sometime don’t honor the DNS TTLs recommendations made by the DNS Authoritative Servers that causes an unexpected user experience. The solution to this problem is to force the client machines to clear the local DNS cache as given below:
MS Windows:
a. Go to Start > Run
b. Type: cmd [enter]
c. At the prompt type: ipconfig /flushdns
MAC:
a. Open a terminal window
b. Type: lookupd –flushcache
LINUX / UNIX: It depends on the DNS caching software used on the client machines.
Restart NSCD
sudo /etc/init.d/nscd restart, OR
service nscd restart
Restart DNSMASQ
sudo /etc/init.d/dnsmasq restart, OR
service dnsmasq restart
Restart BIND
/etc/init.d/named restart, OR
service named restart
Don’t forget the power and use cases of /etc/hosts file on client machines that is by default overrides the external DNS name to IP address mapping.
The minimum hops for resolving a site domain suchna.com are ROOT Name Servers, Top Level Registrars, DNS Authoritative Servers, DNS Name Resolvers and Client Machines.
The Time To Live(TTLs) settings at the DNS Authoritative Server or also referred as Master DNS Server / SOA owner for a site domain and/or internet service address recommends the client machines and DNS name resolvers for refreshing intervals for a name to IP address mapping.
The settings at the client machines sometime don’t honor the DNS TTLs recommendations made by the DNS Authoritative Servers that causes an unexpected user experience. The solution to this problem is to force the client machines to clear the local DNS cache as given below:
MS Windows:
a. Go to Start > Run
b. Type: cmd [enter]
c. At the prompt type: ipconfig /flushdns
MAC:
a. Open a terminal window
b. Type: lookupd –flushcache
LINUX / UNIX: It depends on the DNS caching software used on the client machines.
Restart NSCD
sudo /etc/init.d/nscd restart, OR
service nscd restart
Restart DNSMASQ
sudo /etc/init.d/dnsmasq restart, OR
service dnsmasq restart
Restart BIND
/etc/init.d/named restart, OR
service named restart
Don’t forget the power and use cases of /etc/hosts file on client machines that is by default overrides the external DNS name to IP address mapping.
Category: Technologies
Posted by: bagheljas
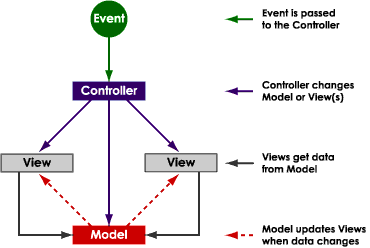
Model-View-Controller (MVC) is a classic software design pattern commonly used for applications that need the ability to maintain multiple views of the same data. The MVC pattern creates a clean separation of objects into one of three categories — models for maintaining data, views for displaying all or a portion of the data, and controllers for handling events that affect the model or view(s). The separation promotes independent innovation for models, views, and controllers.
Events cause a controller to change a model, view, or both. Dependent views are automatically updated whenever a controller changes an underlying model’s data or properties. Similarly, whenever a controller changes a view, for example, by revealing areas that were previously hidden, the view gets data from the underlying model to refresh itself.
Events cause a controller to change a model, view, or both. Dependent views are automatically updated whenever a controller changes an underlying model’s data or properties. Similarly, whenever a controller changes a view, for example, by revealing areas that were previously hidden, the view gets data from the underlying model to refresh itself.
Category: Technologies
Posted by: bagheljas
eXtensible Markup Language (XML) is invented to share and store data independent of platforms and technologies. XML has emerged as the de-facto standard for configurations and data services of new generation applications due to its simplicity and portability.
An XML document contains element(s). An element may have simple text, other element(s), and attribute(s).
The following XML technologies are created to define, manage, and use of data stored in XML:
An XML document contains element(s). An element may have simple text, other element(s), and attribute(s).
The following XML technologies are created to define, manage, and use of data stored in XML:
- Document Type Definition (DTD) defines the legal building blocks, the elements and attributes of an XML document. DTD didn't address what values (i.e. data type) these elements and attributes can have.
- XML Schema Definition (XSD) is also used to define the legal building blocks, the elements and attributes of an XML document, just like a DTD but XML Schemas has support for data types and namespaces.
- XML Namespaces provides a method to avoid element name conflicts.
- XML Query Language (XQuery) plays the same role as SQL plays for RDBMS.
- XML Path Language (XPath) provides a method to directly select nodes or node-sets in an XML document. It is the foundation for XSLT.
- XML Linking Language (XLink) defines a standard way of creating hyperlinks in XML documents.
- XML Pointer Language (XPointer) allows the hyperlinks to point to more specfic sections of the XML document.
- eXtensible Stylesheet Language Transformations (XSLT) facilitates xml document transformations into XHTML, other XML, text, and various other format document.
Category: Technologies
Posted by: bagheljas
- Increased Design and Layout Capabilities
- Centralize Style Specifications
- Increased Throughput form Network and Web Server
Category: Technologies
Posted by: bagheljas
- Linked : a separate style sheet document that can be linked from any HTML document. Override only HTML.
<head>
<link href="mystyle.css" rel="stylesheet"/>
</head> - Embedded: a block of code that apply to the html document only. Override Linked Styles and HTML.
<style>
<!--
H1 {font-size: 16pt; text-align:center}
-->
</style> - Inline: declare styles directly in an HTML tag and applicable to the content of the tag. Override all other style declarations.
<H1 style="font=style: italic"> HeadingOne </H1>
Disclaimer
The views expressed in the blog are those of the author and do not represent necessarily the official policy or position of any other agency, organization, employer, or company. Assumptions made in the study are not reflective of the stand of any entity other than the author. Since we are critically-thinking human beings, these views are always subject to change, revision, and rethinking without notice. While reasonable efforts have been made to obtain accurate information, the author makes no warranty, expressed or implied, as to its accuracy.