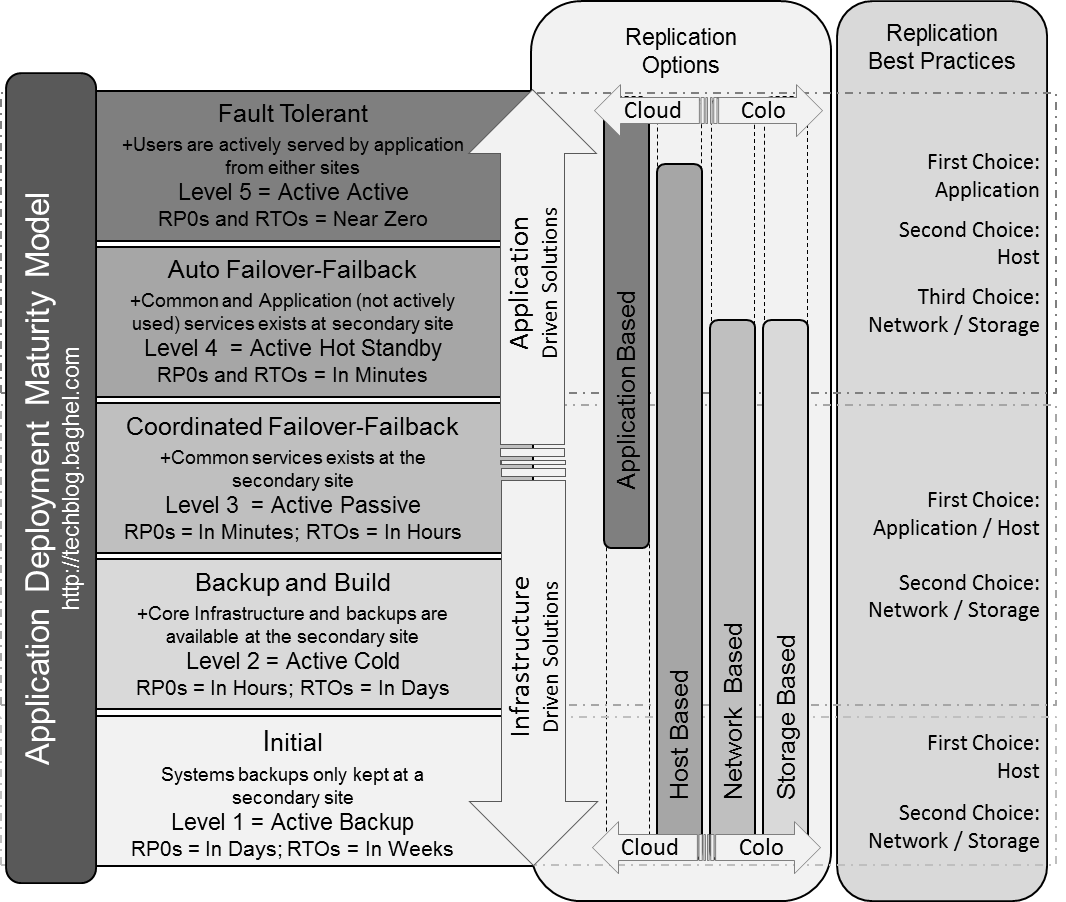
Category: Best Practices
Posted by: bagheljas
Availability and Applications of Data have emerged as a business innovation engine of the present time and for the foreseeable future.
Data Platforms are a conglomerate of Business Requirements, Architectures, Tools & Technologies, Frameworks, and Processes to provide Data Services. Hence, the Data Platform Innovation foundation is from people, processes, and technology managing and utilizing an enterprise Data Platform. In the article, I have organized the emerging Industry Leading Practices into seven Pillars to maximize data value at speed in an enterprise environment.
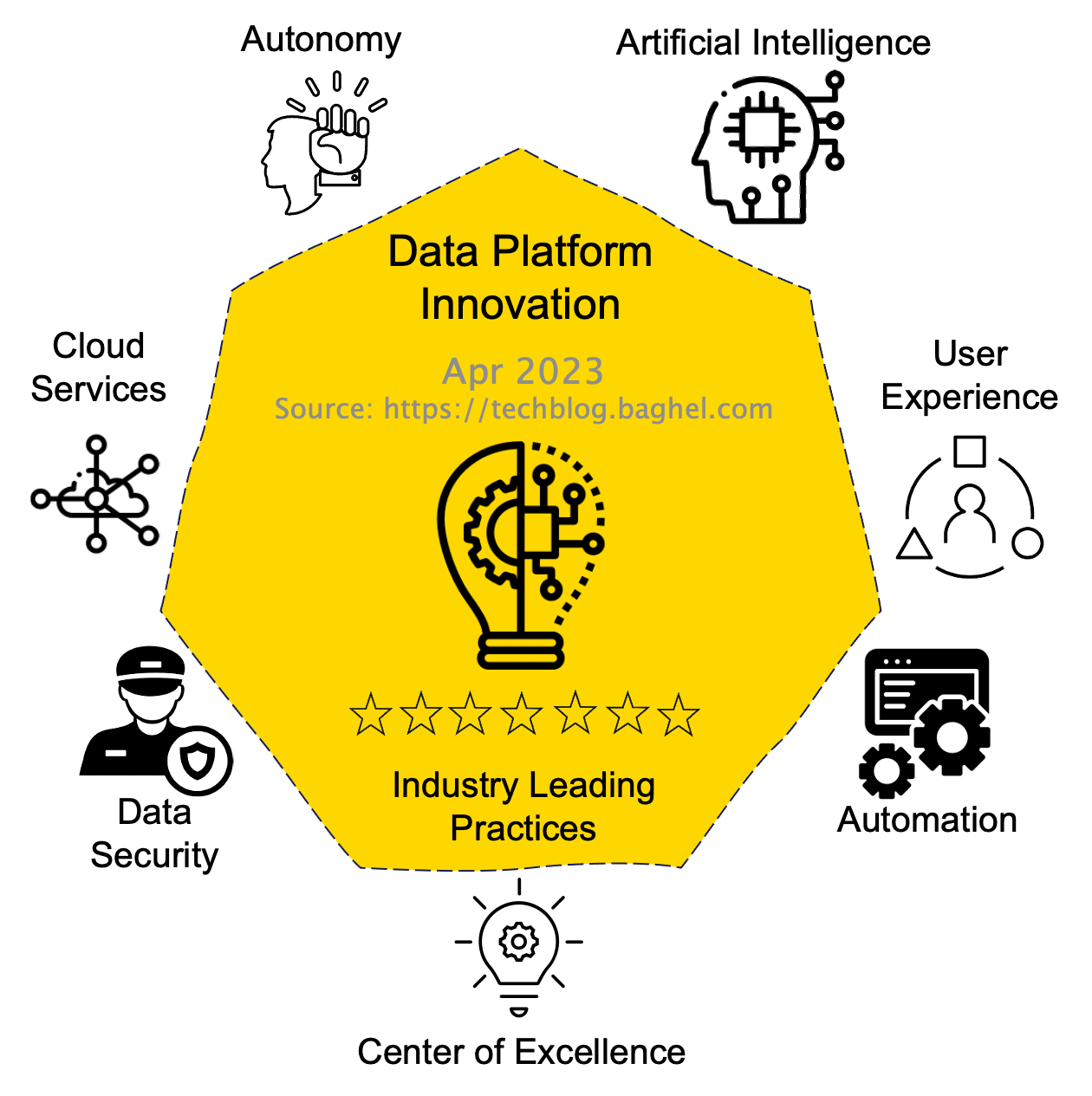
Pillars - Data Platform Innovation: Industry Leading Practices
Data Platforms are a conglomerate of Business Requirements, Architectures, Tools & Technologies, Frameworks, and Processes to provide Data Services. Hence, the Data Platform Innovation foundation is from people, processes, and technology managing and utilizing an enterprise Data Platform. In the article, I have organized the emerging Industry Leading Practices into seven Pillars to maximize data value at speed in an enterprise environment.

Pillars - Data Platform Innovation: Industry Leading Practices
- Autonomy
- Implement Data as a Product with an operating model that establishes data product owner and team.
- Support Data Democratization utilizing Distributed Data Architecture and Data Mesh.
- Enable end-to-end service delivery ownership to the Data product owner.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- Create a raw Data copy availability to enable AI Data Models yet to be discovered.
- Utilize AI Tools to manage Data identification, correction, and remediation of Data quality issues.
- User Experience
- Create and manage data literacy and data-driven cultural activities for employees to learn and embrace the value of data.
- Enable data navigation and data research tools for employees.
- Automation
- Utilize DataOps at the heart of provisioning, processing, and information management to deliver real-time use cases.
- Implement automatic backup and restoration of Data and digital twins of the Data estate.
- Center of Excellence
- Shift from stakeholders' buy-in approach to delivery partners' approach that finds and enables innovation.
- Create Data Eco-System utilizing Data Alliances, Data Sharing Agreements, and Data Marketplace to develop an Enterprise Data Economy.
- Publish Common Data Models, Policies, and Processes to promote ease of collaboration within and across organizations.
- Data Security
- Contribute actively to individual data-protection awareness and rights.
- Communicate the importance of data security throughout the organization.
- Develop Data privacy, Data ethics, and Data security as areas of competency, not just to comply with mandates.
- Cloud Services
- Cloud First mindset for quickly exploring and adopting innovation at speed with minimal sunk cost once that becomes mainstream. Let the business model drive the Cloud equilibrium.
- Enable cloud for flexible data model tools supporting querying for unstructured data.
- Enable edge devices and high-performance computing available at Data sources to deliver real-time use cases.
Category: Best Practices
Posted by: bagheljas
Industry-leading Process uniquely establishes the People, Process, and Technology popularly known as PPT Models for the Deployment Model, Operating Model, and Center of Excellence for the enterprises for the new implementations of an Enterprise Data Platform. While for the existing Enterprise Data Platform, we review and revise these Models. The process consists of three phases Assess, Deploy, and Operate.
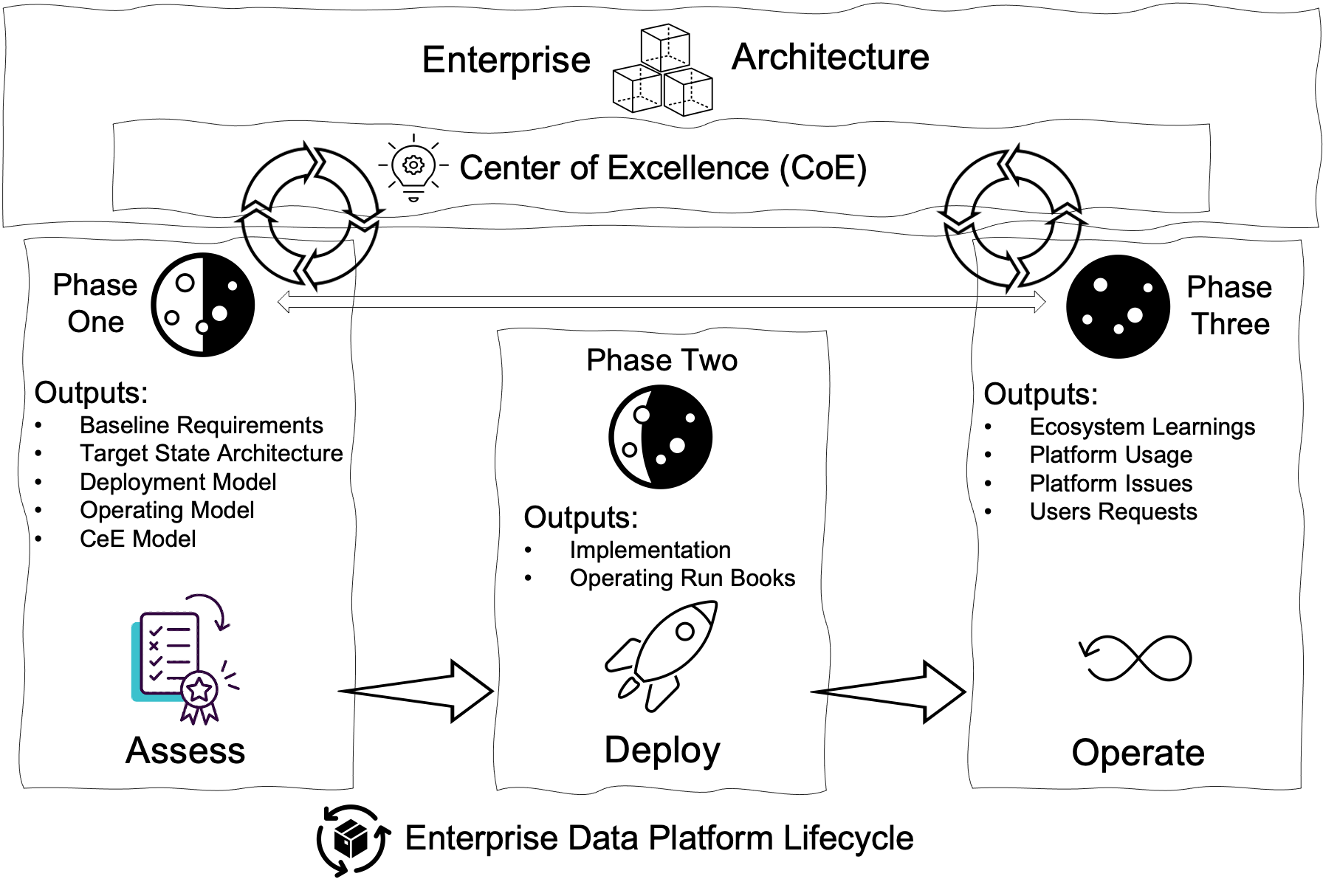
I strongly believe in that Enterprise Data Platform Modernization is an Enterprise Journey, not a Milestone. Hence, the process loops back inputs from the Operating Model and Center of Excellence to review and revise PPT Models of the Deployment Model, Operating Model, and Center of Excellence for the Enterprise Data Platform. We highly recommend performing this minimum of twice a calendar year due to the speed and volume of innovations in the data domain.

Category: Best Practices
Posted by: bagheljas
Industry Leading Approach is to create an Enterprise Data Economy built on Data Collaboration, Data Democratization, and improved User Experiences for Data Research and Artificial Intelligence. It has ingrained Data Privacy, Security, and Resiliency capabilities. The solution design uses the following guiding principles those are from the article, Data Platform Innovation: Industry Leading Practices.
Use Reference Architecture from the article, Data Platform Buzzwords: Introduction and So What?, to assess and design the Data Platform Target State Architecture.
- Cloud First while extracting the life of current IT investments
- Utilize Data Ops to automation for Data Services and Backup & Restore Data
- Utilize Distributed Data Architecture and Data Mesh for Data Democratization
- Design for real-time use cases and ease of data research tools integration
- Flexible Data Stores with anytime availability of the Raw Data
- Identify and Use AI Tools to Handle Data Quality Issues
- Utilize Data Hub, Data Fabric, and Data Navigation for ease of Data Discovery and Collaboration
Use Reference Architecture from the article, Data Platform Buzzwords: Introduction and So What?, to assess and design the Data Platform Target State Architecture.
10/19: Web Application Security
Category: Best Practices
Posted by: bagheljas
Category: Best Practices
Posted by: bagheljas
Category: Best Practices
Posted by: bagheljas
Change is inevitable for an enterprise application life cycle. The change for an enterprise application comes in various forms and the most common words used for the application changes are migration, transition, transformation, upgrades and consolidation. The diagram below creates a layered architecture for an enterprise application changes named as Enterprise App Migration Layers. The Enterprise App Migration Layered Architecture provides a cross industry standard approaches for application migration needs.
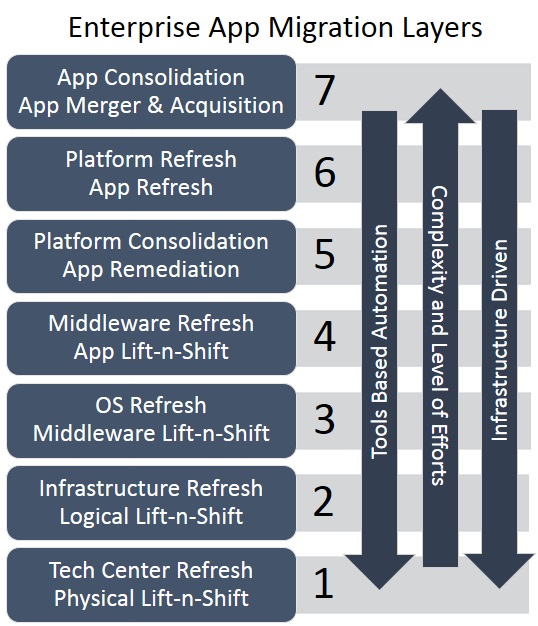
It is leading practice to limit number of layers changing for a given migration event to keep the migration simple as much as possible. In contrary, you get economies of scope benefits to combine the changes in multiple layers. Therefore, selecting changes for a migration event is an art and science that needs to combine with the capabilities, refresh requirements (usually driven around app platform components end of life timelines), timeline objectives and cross functional resources availability.

It is leading practice to limit number of layers changing for a given migration event to keep the migration simple as much as possible. In contrary, you get economies of scope benefits to combine the changes in multiple layers. Therefore, selecting changes for a migration event is an art and science that needs to combine with the capabilities, refresh requirements (usually driven around app platform components end of life timelines), timeline objectives and cross functional resources availability.
- 7. App Consolidation - App Merger & Acquisition: When an enterprise have more then two applications serving one functional domain that either applications is capable to serve functional users. In this case, enterprise architect often port less desired application stack to the most desired application stack. On the other hand, if a functional domain is matured and common in industry that has an economical Cloud Computing Software as a Service (SaaS) provider(s) that meets your functional, performance and security requirements. An enterprise architect may consider to migrate to a SaaS provider. It is a leading practice to develop and execute comprehensive testing plan with multiple domains such as features, system, integration, security, performance, backup & disaster recovery and user acceptance. This layer migration usually driven by top down enterprise IT strategy with or without cloud.
- 6. Platform Refresh - App Refresh: You are refreshing application COTS product to latest version or adding new components for new features either on existing or latest versions of underlying technology stack. The migration is manual in nature but one may consider build automation. It is a leading practice to develop and execute testing plan in domains such as features, system, integration, and user acceptance.
- 5. Platform Consolidation - App Remediation: You are retaining application COTS product version and functionality but porting underlying technology stack to desired vendors to comply with enterprise architecture mandates such as DB2 to Oracle, WebLogic to Tomcat, IIS to Apache etc. The migration is manual in nature but one may consider build automation. The most common type of migration when an enterprise is looking to eliminate expensive technology components from the enterprise technology portfolio or migrating to Public Cloud Computing - Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) provider. It is a leading practice to develop and execute testing plan in domains such as features, system, performance, integration, and user acceptance.
- 4. Middleware Refresh - App Lift-n-Shift: You are retaining application COTS product version and functionality but upgrading the underlying middleware technologies to latest version such as Oracle DB, WebLogic AS and Apache WS. The migration is manual in nature but one may consider build automation. It is a leading practice to develop and execute testing plan in domains such as system, security, performance, integration, and user acceptance.
- 3. OS Refresh - Middleware Lift-n-Shift: You are upgrading versions of underlying operating system or migrating to an standardize operating system image of existing version. One may consider tools like AppZero or manual transformation. The most common migration type when an enterprise is changing and/or outsourcing to managed hosting provider. It is a leading practice to develop and execute testing plan in domains such as system, security, integration, and user acceptance.
- 2. Infrastructure Refresh - Logical Lift-n-Shift: You are refreshing server hardware platform only. It is a leading practice to leverage tools to perform Logical Lift-n-Shift migration. The industry leading tools for such migration are PlateSpin Migrate, Rackware, VMWare Tools, and Data Gardens. It is common to hear the terms like P2P, P2V, V2P and V2V migrations for this kind of exercise. The most common migration type when you are migrating to Cloud Computing - Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) provider.It is a leading practice to develop and execute testing plan in domains such as system, security, performance, integration, and user acceptance.
- 1. Tech Center Refresh - Physical Lift-n-Shift: You are either moving from on-premise data center to colocation or changing colocation provider only. It is a leading practice to develop and execute testing plan in domains such as integration, and user acceptance.
Category: Best Practices
Posted by: bagheljas
Category: Best Practices
Posted by: bagheljas
Cloud Readiness of an application system deployment in IaaS service model is dependent on the following factors:
- Technology: Operating systems and middleware technologies are capable to run on x86 server architecture platform also known as x86 server platform. The most commonly used operating systems over x86 server platforms are Windows and Linux operating systems and widely available as IaaS from several vendors such as Savvis, Rackspace, Terremark, and Amazon.
- Implementation: We often find that our implementation is not compatible to run on x86 server platform and have direct dependency on the server hardware platform. In order to be cloud ready, it needs to be on a x86 server platform with no direct dependency on the server hardware platform.
- License and Support: This one tightly aligns with the products used for implementing the application. Product vendor needs to support and economical license options for an application system deployment in a public and private cloud deployment. You may find that to overcome of license constraint people produce a dedicated cluster for certain technology component such as Oracle Database.
- Scale and Performance: The public cloud vendors normally will not guarantee the performance for disk and network IO. You will find dedicated CPU and Memory with System Availability commitments from the public cloud vendors. If an organization got its own scale to operate and has strict performance requirements around disk and network IO and doesn’t need to scale (beyond pre-defined limits) without a lead time are implementing a managed private cloud.
- Security Mandates: The most difficult security mandates to meet by a public cloud vendor is that my data needs to stay physically separated from others. In that case, you are required to implement a private cloud. The security mandates that requires data to be encrypted over wire and rest and who can access can be met by a public cloud vendor offering using software based controls. We may find that organization go for a hybrid model where you hand pick what to share (software controls meets your security mandates) and what you won’t (you will need to have hardware controls in place to meet your security mandates). Cloud provider such as Savvis specializes in the creating the Hybrid System Deployment to meet the Enterprise Cloud Computing (ECC) needs.
Category: Best Practices
Posted by: bagheljas
First of all, let's understand Enterprise Service Oriented Architecture (SOA). In nutshell, the service catalog for an enterprise SOA is built for re-usability by multiple internal and external consumers, not for mere system integration for a single consumer.
The Enterprise SOA adoption strategy pillars are Platform Value, Platform Commitment, and Platform Activities. Using these pillars, one can develop SOA adoption strategy and plan that suit their organization values and culture:
The Enterprise SOA adoption strategy pillars are Platform Value, Platform Commitment, and Platform Activities. Using these pillars, one can develop SOA adoption strategy and plan that suit their organization values and culture:
- Platform Values: Ability to deliver quality products faster and cheaper. For business, it is all about economies of scope and scale. For IT, it is plug and plays development as much as possible that is not re-inventing the wheels. In other words, re-usability.
- Platform Commitments: To win application owners support and confidence the platform needs to make commitments to be available, scalable and backward compatible.
- Platform Activities: Establish SOA collaboration, not just governance. Create continuous education for business and IT. Catch at the conception to onboard new applications and proactively refine service catalog to onboard new and existing applications.
Category: Best Practices
Posted by: bagheljas
Data Center Migration Project (DCMP) are usually expensive and considered risky. I personally believe and proved several times that it is an opportunity to improve infrastructure deployment and exercise standardization & tech refresh as economies of scope than just refreshing compute, storage and network platform. We mostly find that most organizations just limit the scope of DCMP to refresh compute, storage and network platform and miss the huge opportunity to kill multiple birds in one shot.
Data Center Migration Project Strategy pillars are Migration Waves, Migration Methods and Migration Validations. Using these pillars, one can develop DCMP strategy and plan that's suits their organization values, culture and applications portfolio:
Data Center Migration Project Strategy pillars are Migration Waves, Migration Methods and Migration Validations. Using these pillars, one can develop DCMP strategy and plan that's suits their organization values, culture and applications portfolio:
- Migration Waves: It is critical to divide your application portfolio into multiple waves based on business, application and team needs. At the minimum, you are at least planning two Migration Waves for a DCMP. Usually the first wave that is also known as Wave Zero consist of standing up core infrastructures of compute, storage and network with core system services such as DNS / GTMs, AD / Single-Sign-On, Firewalls Stage One, L4 Load Balancers / LTMs, Mail Relays, Monitoring, Central Logging, Outbound Proxy, Backup and Recovery, and Misc Services (VPN, SVN, Terminal Servers, Jump Servers). These core systems services usually could co-exists with current production either independently or in-collaboration.
- Migration Methods: Selecting a method is key that is dependent on availability needs of business function, application design, tools capabilities and skills of the team. The commonly known methods are first green field build, second clone the currently running production server from backup and third clone the currently running production server fresh. Each migration method has costs, benefits and risk associated with it.
- Migration Validations:I usually refer this as minimum verification plan that needs to created carefully. We all do great jobs with specific verticals and the migration issues falls in cross-boundary. Identify and develop cross-boundary validation and have an enterprise solutions architect (who understands applications and infrastructures components) available to provide the technical oversight for solving cross-boundary issues faster and cheaper.
Disclaimer
The views expressed in the blog are those of the author and do not represent necessarily the official policy or position of any other agency, organization, employer, or company. Assumptions made in the study are not reflective of the stand of any entity other than the author. Since we are critically-thinking human beings, these views are always subject to change, revision, and rethinking without notice. While reasonable efforts have been made to obtain accurate information, the author makes no warranty, expressed or implied, as to its accuracy.